Yes, the UW is a participating member of eduroam. This means:
- UW faculty, staff and students visiting other eduroam participating institutions can access eduroam using their UW NetID credentials.
- Visitors from other eduroam enabled institutes can access the eduroam network at UW for secure wireless access to the Internet.
The eduroam SSID will show up in your wireless connections on your mobile device or laptop.
Eduroam is a free service provided by an international federation of academic institutions for all members of the worldwide research and education community.
Eduroam works by sending your device certificate through a ‘tunnel’ back to the UW to be authenticated. Once your certificate has been verified by UW, that information is returned to the institution you are visiting so you can access the eduroam wireless network.
For example, if you were visiting the University of Oregon, your device would automatically log in to the eduroam wireless network using your device’s certificate. This certificate is sent to the UW’s identity management systems to be authorized, and a message is sent back to the University of Oregon advising that your certificate is authorized and you are allowed access to eduroam network.
Eduroam utilizes WPA2 Enterprise encryption and 802.1X EAP-TLS authentication to ensure your data security during transmissions over the wireless medium.
However once your data transitions over to the wired medium or local network, you should be aware that any local security measures at that institution will apply to you as well.
For example, the firewall policies at the visited institution may be different from those at your home institution, and as a visitor, you may have access to fewer services and resources on the Internet than you would normally.
Yes, UW faculty, staff, and students can access the eduroam service on any of the three UW campuses, UW Medicine and other UW Wi-Fi locations where the SSID is present.
Yes, if the institution you are visiting is a participating member of eduroam, you will have access. Before using eduroam, you will first have to configure your device for eduroam via http://onboard.wifi.uw.edu.
Most commonly this is a configuration issue on your device. Please contact the IT services at your home institution for more information first.
If the eduroam SSID does not appear in your wireless connections list, first check that:
- There are other wireless networks available (there could be a problem with your device).
- Your device is in range of the eduroam network. Eduroam is currently available at all UW-IT supported Wi-Fi locations.
If both of these are correct, you’ve contacted IT services at your home institution and you are still having problems connecting to the eduroam network, please contact UW-IT Help so they can investigate the issue further.
Yes, we offer access to ANYROAM which is a complementary service to eduroam aproviding login credentials to people who are not associated with an existing eduroam institution. ANYROAM is not meant to be used by people with eduroam access through their home institution and will conflict with the existing configuration and possibly prevent access. ANYROAM is an opt-in service and not all eduroam providers support ANYROAM.
Follow the instructions at the Connecting to ANYROAM to begin using ANYROAM.
NOTE: If you already use eduraom, then DO NOT try to configure your device for ANYRAOM as it will create problems with accessing eduroam.
Support for ANYROAM is available here
No. You only need to onboard your device once and it will remember your settings for the next time you’re in eduroam range.
Yes. Just make sure you have some sort of Internet connection (home, coffee shop, tethered to cell, etc) and onboard via http://onboard.wifi.uw.edu. You will get a connection failed message, however, the profile will have been installed and when you’re next in range of eduroam, your device will connect.
The exception is macOS which will require you to follow the usual onboard instructions at http://onboard.wifi.uw.edu and once you’re in range of eduroam, you will need to manually click the “eduroam” SSID in the macOS wireless manager. You will then be prompted to enter your local user account password (the one you use to login to the computer), then click “Always Allow”. This will only be required on your first connection.
You can however it is not supported. Running the onboarding software utility ensures correct certificate, network and security profile configurations get installed on the client device.
You can add these settings manually by creating the new profile and security settings for the eduroam SSID, however, UW-IT doesn’t recommend or support manual configurations of client devices or provide documentation. To manually onboard your device go to http://onboard.wifi.uw.edu and choose “Non-specific OS” under device selection and follow the instructions.
Yes, you need to onboard again after a UW NetID change.
No, you do not need to onboard again after a password change.
Your device certificate will be valid for 4 years from the creation date. You will receive an email notification from our onboarding vendor, Secure W2, at 30, 15, 7, 2 and 1 day prior to expiration. This email will include the MAC address of the device that requires the updated certificate. You should re-onboard your device before the certificate expires by going to https://onboard.wifi.uw.edu.
You can compare the serial numbers and fingerprints of the certificates sent to you by our RADIUS servers and installed by SecureW2 JoinNow with the details below.
The supplicant on your device uses root and intermediate certificates to create a “chain of trust” to the server certificate. This validates the RADIUS server is trusted.
You will also have a device certificate and private key installed on your device which will be signed by “University of Washington Device Intermediate CA”. This certificate is what RADIUS uses to identify and authorize your device.
Please note that the certificate expiry date and time maybe look different depending on your timezone. It is recommended to compare the fingerprints if you’re unsure.
- radius.uw.edu
- Server certificate
- Expires: Thursday, May 16, 2024 at 4:59:59 PM Pacific Daylight Time (11:59:59 PM UTC)
- Serial Number: 00 AE 4A FF 31 E3 4F 39 E8 1C 7F BF 36 5C AE A2 29
- SHA-256: 32 0E 94 53 70 E6 B5 38 26 64 D7 73 A6 BA 28 EF BF 2E A6 B6 54 14 10 11 CB A4 10 A3 E1 96 11 70
- SHA-1: 0B 16 62 67 94 31 88 EF 0B 18 F2 CF 8D 2D E1 58 4B AC D2 7D
- InCommon RSA Server CA
- Intermediate certificate authority
- Expires: Wednesday, October 5, 2024 at 4:59:59 PM Pacific Daylight Time (11:59:59 PM UTC)
- Serial Number: 47 20 D0 FA 85 46 1A 7E 17 A1 64 02 91 84 63 74
- SHA-256: 0A 05 C4 62 75 63 90 DD 1F 1D 5D D8 27 94 C3 00 F0 4B E7 89 DC E7 6D 7E 31 2F 79 0D 68 FD 38 5A
- SHA-1: F5 FB 01 DE A6 E5 9C A6 DD 05 70 54 F4 A3 FF 72 DD E1 D5 C6
- Intermediate certificate authority
- USERTrust RSA Certification Authority
- Root certificate authority
- Expires: Monday, January 18, 2038 at 3:59:59 PM Pacific Standard Time (23:59:59 PM UTC)
- Serial Number: 01 FD 6D 30 FC A3 CA 51 A8 1B BC 64 0E 35 03 2D
- SHA-256: E7 93 C9 B0 2F D8 AA 13 E2 1C 31 22 8A CC B0 81 19 64 3B 74 9C 89 89 64 B1 74 6D 46 C3 D4 CB D2
- SHA-1: 2B 8F 1B 57 33 0D BB A2 D0 7A 6C 51 F7 0E E9 0D DA B9 AD 8E
- Root certificate authority
Certain older generation Windows-based Intel wireless adapters are unable to see Wi-Fi 6/802.11ax networks unless their drivers have been updated. This means that your device may not be able to connect to the Wi-Fi in any buildings that are running the latest generation Wi-Fi Access Points.
You can view the advisory from Intel here or download the automated Intel® Driver & Support Assistant here. If the driver assistant doesn’t find your driver, you may need to manually download it from the Intel website.
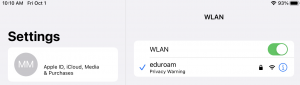
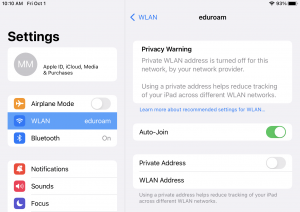
Apple’s release of iOS14 brought some changes to the way your device identifies itself to Wi-Fi networks.
This change causes the device to create a randomized “Private Address” as its MAC address which will cause the UW Wi-Fi network to treat it as a brand new device each time a new Wi-Fi profile is created. This Private Address further complicates any troubleshooting support UW-IT can provide.
For these reasons, the onboarding tool turns the Private Address feature off.
Firstly, take a look at our Wi-Fi Advisories page and our Eduroam Guides page.
Otherwise, please follow the steps below which fix the most common problems.
1) Ensure the date and time is correct on your device.
2) Ensure your device software and wireless drivers are up to date.
3) Ensure your UW NetID is correctly enrolled to receive eduroam access.
- Navigate to https://uwnetid.washington.edu and enter your UW NetID and password.
- On the left side of the screen under “Manage <your UW NetID>”, click on Computing Services.
- Ensure that “Eduroam Radius Access” is enabled under the Active Services.
- If the service is listed under the Inactive Services, click the check box and hit the Subscribe button to add it to your active services. Wait for 15 minutes and you should be able to access the eduroam service.
4) Remove the eduroam Wi-Fi profile on your device and re-onboard. We have guides available for the most common devices on our Eduroam Guides page.
Can’t find what you’re looking for?
If these instructions do not resolve your issue, please contact UW-IT using the form linked below.